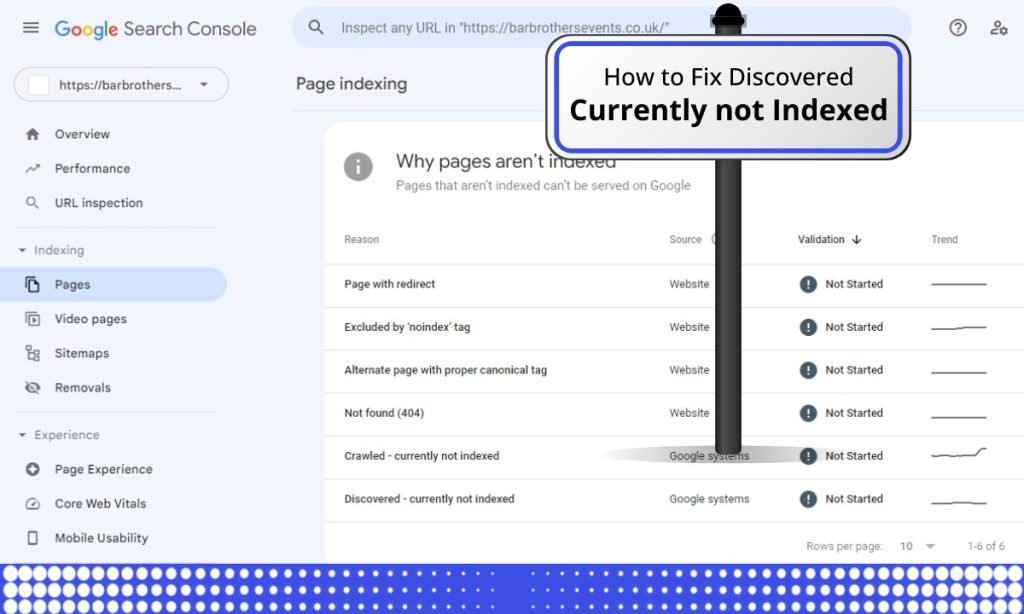
The “Discovered – currently not indexed” is an issue that appears in Google Search Console when Google’s crawlers have found a page on your website, but it has not been added to the search index yet. This means that the page can’t be found when someone searches for it on Google.
This is what Google has to say about Discovered currently not indexed.

If you have discovered “currently not indexed” errors in Google Search Console, it means that Google has encountered difficulties indexing certain pages of your website. Here are some steps you can take to address and fix these errors:
General Guidelines to fix Discovered – currently not indexed
- Verify the issue: Confirm that the pages in question are indeed not indexed by performing a site search on Google. Use the “site:” operator followed by your domain name (e.g., site:example.com). If the pages do not appear in the search results, it confirms the indexing problem.
- Check for indexing restrictions: Ensure that there are no intentional restrictions preventing Google from indexing your pages. Check the “robots.txt” file on your website’s root directory and make sure it doesn’t disallow crawling or indexing of the affected pages.
- Verify XML sitemap: Confirm that the affected pages are included in your XML sitemap. An XML sitemap helps search engines discover and index your website’s pages more efficiently. If the pages are missing from the sitemap, add them to it and submit the updated sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Evaluate crawlability: Examine the affected pages for any technical issues that might impede Google’s ability to crawl and index them. Check for common problems such as server errors (e.g., 5xx status codes), slow page load times, or excessive use of “noindex” tags.
- Improve content quality: Ensure that the content on the affected pages is of high quality and provides value to users. Poorly written or thin content may be disregarded by Google’s indexing algorithms. Enhance the content by adding relevant and unique information, optimizing meta tags, and incorporating target keywords naturally.
- Fix technical issues: Address any technical problems that might hinder indexing. Examples include broken internal links, JavaScript or CSS errors, duplicate content, or improper canonicalization. Correct these issues to improve the overall crawlability and indexing of your website.
- Fetch and render: Use the Fetch as Google tool in Google Search Console to check how Googlebot sees and renders the affected pages. This helps you identify any rendering issues or blocked resources that could prevent proper indexing.
- Increase external visibility: Promote the affected pages through various marketing channels to increase their visibility and attract more external links. Quality backlinks from reputable websites can help improve the indexing and ranking of your pages.
- Monitor changes and request reindexing: After implementing the necessary fixes, keep an eye on Google Search Console’s indexing reports to ensure the “currently not indexed” errors are resolved. If the errors persist or you need to expedite the indexing process, you can use the “URL Inspection” tool in Search Console to request reindexing of specific pages.
Remember, it may take some time for Google to re-crawl and reindex the fixed pages. Be patient, monitor the progress, and continue optimizing your website for better indexing and visibility.
Specific Guidelines to fix Discovered – currently not indexed
To fix the “Discovered – currently not indexed” error in special cases, you can follow the below steps:
- If the website is old (6-12 months of age or more) and the reported URLs have been created almost 4 weeks ago then follow these steps:
- Check if the reported URLs are important for your website and accessible to Google then start validation straightaway. The validation will be passed.
- If the pages are low-quality such as /feed URLs or .atom URLs then you can ignore them. I normally prefer removing /feed and /or atom URLs from the website source code and no index them to avoid these URLs from getting crawled.
- If the reported URLs are a mixture of low-quality/unwanted and important pages then list the important pages and use request indexing or API indexing tool. You can also follow the steps mentioned below to index the important URLs. I don’t start the validation in this case because it fails due to unwanted URLs. I don’t see /feed or .atom URLs indexed so validation gets failed.
You can hire our technical SEO services, If you need assistance in fixing discovered-currently not indexed issues. Feel free to comment and share your experience.